백준 13565번 C++ 풀이
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/13565
13565번: 침투
첫째 줄에는 격자의 크기를 나타내는 M (2 ≤ M ≤ 1,000) 과 N (2 ≤ N ≤ 1,000) 이 주어진다. M줄에 걸쳐서, N개의 0 또는 1 이 공백 없이 주어진다. 0은 전류가 잘 통하는 흰색, 1은 전류가 통하지 않
www.acmicpc.net
| 시간 제한 | 메모리 제한 | solved.ac 티어 |
| 1초 | 512MB | 실버 2 |
문제
인제대학교 생화학연구실에 재직중인 석교수는 전류가 침투(percolate) 할 수 있는 섬유 물질을 개발하고 있다. 이 섬유 물질은 2차원 M × N 격자로 표현될 수 있다. 편의상 2차원 격자의 위쪽을 바깥쪽(outer side), 아래쪽을 안쪽(inner side)라고 생각하기로 한다. 또한 각 격자는 검은색 아니면 흰색인데, 검은색은 전류를 차단하는 물질임을 뜻하고 흰색은 전류가 통할 수 있는 물질임을 뜻한다. 전류는 섬유 물질의 가장 바깥쪽 흰색 격자들에 공급되고, 이후에는 상하좌우로 인접한 흰색 격자들로 전달될 수 있다.
김 교수가 개발한 섬유 물질을 나타내는 정보가 2차원 격자 형태로 주어질 때, 바깥쪽에서 흘려 준 전류가 안쪽까지 침투될 수 있는지 아닌지를 판단하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
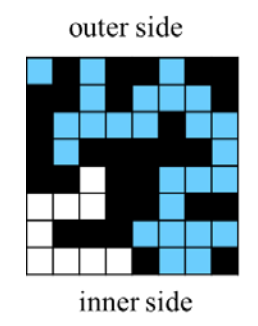 |
 |
| (a) The current percolates. | (b) The current does not percolate. |
예를 들어, Figure 1(a) 에서는 바깥쪽에서 공급된 전류가 안쪽까지 침투하지만, Figure 1(b)에서는 그렇지 못한다.
입력
첫째 줄에는 격자의 크기를 나타내는 M (2 ≤ M ≤ 1,000) 과 N (2 ≤ N ≤ 1,000) 이 주어진다. M줄에 걸쳐서, N개의 0 또는 1 이 공백 없이 주어진다. 0은 전류가 잘 통하는 흰색, 1은 전류가 통하지 않는 검은색 격자임을 뜻한다.
출력
바깥에서 흘려준 전류가 안쪽까지 잘 전달되면 YES를 출력한다.
그렇지 않으면 NO를 출력한다.
전형적인 그래프 탐색 문제이다. 맨 아래(inner side)에서 출발하여 맨 위(outer side)로 가는 경로가 있는지 조사하면 된다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
void input() {
cin >> m >> n;
graph.resize(m);
string input;
for(auto& row : graph) {
cin >> input;
for(char x : input) row.push_back(x - '0');
}
}
// 41192KB / 36ms
bool dfs(int st_x, int st_y) {
if (st_y == 0) return true;
graph[st_y][st_x] = -1;
bool result = false;
int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int next_x = st_x + dx[i];
int next_y = st_y + dy[i];
if(next_x < 0 || next_x >= n || next_y < 0 || next_y >= m) continue;
if (graph[next_y][next_x] == 0) result = result || dfs(next_x, next_y);
if (result) return true;
}
return false;
}
// 6000KB / 20ms
bool bfs(int st_x) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
q.push({st_x, m - 1});
graph[m - 1][st_x] = -1;
while(!q.empty()) {
auto [cur_x, cur_y] = q.front();
q.pop();
if (cur_y == 0) return true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int next_x = cur_x + dx[i];
int next_y = cur_y + dy[i];
if(next_x < 0 || next_x >= n || next_y < 0 || next_y >= m) continue;
if (graph[next_y][next_x] == 0) {
graph[next_y][next_x] = -1;
q.push({next_x, next_y});
}
}
}
return false;
}
void sol() {
for(int x = 0; x < n; x++) {
if (graph[m - 1][x] == 0) {
// if (bfs(x)) {
if (dfs(x, m-1)){
cout << "YES";
return;
}
}
}
cout << "NO";
}
int main () {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
input();
sol();
}
